Building Social Emotional Learning
Building SEL encompasses understanding and managing emotions, setting positive goals, showing empathy for others, nurturing rewarding relationships, and making responsible decisions. It forms the bedrock of not just a well-rounded education, but a thriving, successful life.
But why should we care about SEL in our classrooms? It’s simple, really. SEL is intricately linked to student success, both inside and outside the school environment. When students are emotionally intelligent, they’re better equipped to handle the stress of exams, work collaboratively in teams, and steer through the many social challenges of school life. Moreover, SEL doesn’t just complement academic learning – it’s part of the very fabric that makes learning stick. It’s the secret sauce that helps students apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios and emerge as true champions of their own learning journey.
Let’s dive deeper to understand how SEL can transform educational experiences and prepare our kids for a brighter, emotionally intelligent future.
How to Be Your Authentic Self: 7 Powerful Strategies to Be True article suggests the path to create the life you want starts with knowing who you are. If you follow these tips to find your authentic self, you’ll begin to light the way forward. The article also provides authentic self examples.
The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Schools
When we talk Social Emotional Learning (SEL), the heart of the matter often lies within the powerful realm of Emotional Intelligence (EI). Far from being just a buzzword, EI is reshaping the way educators approach teaching and the way students engage with learning.
Understanding the Role of Emotions in Learning
It’s vital to recognize that cognition doesn’t happen in an emotional vacuum. Emotions can fuel our motivation, impact our attention, and either enhance or impede our learning processes. By integrating SEL in the classroom, we’re acknowledging that a student’s emotional state is not separate from their ability to learn; it’s actually central to it.
Methods to Enhance Students’ Emotional Intelligence
So, how can schools nurture EI among students? It’s a hands-on process that invites participation, self-reflection, and a lot of practice. Techniques such as role-playing, journaling, and group discussions are not merely exercises but rather keys to unlocking a deeper understanding of oneself and others. Also, fostering a safe and trusting classroom environment encourages students to express and manage their emotions more skillfully.
Measuring the Impact of Emotional Intelligence on School Climate
But it’s not all theoretical. The impact of emotional intelligence on school climate is tangible and measurable. Surveys and observations can reveal shifts in behaviors, a drop in conflicts, and improvements in relationships among peers and between students and teachers. A positive school climate, enhanced by SEL, can lead to better academic outcomes, fewer behavioral problems, and an overall happier, more cohesive educational setting.
- Increased empathy and understanding
- More effective communication skills
- Stronger interpersonal relationships
By embracing the tight-knit connection between emotional intelligence and Social Emotional Learning, schools become more than just places of academic endeavor. They transform into thriving ecosystems where future leaders learn the true value of emotions in shaping their world.
Fostering Empathy and Compassion in Education
Embracing the essence of Social Emotional Learning (SEL) goes beyond mere academic instruction. At its heart, SEL is about cultivating a community where empathy and compassion thrive. When students learn to step into the shoes of others and understand their feelings, they unlock the potential for meaningful connections and cooperative learning.
Empathy and Compassion: Cornerstones of SEL
Empathy and compassion are not just feel-good buzzwords; they’re vital skills for students’ social and emotional toolkit. These two attributes fuel a nurturing environment, where every member of the school community can feel valued and understood.
Classroom Exercises That Promote Understanding and Kindness
- Role-playing activities that encourage students to explore different perspectives
- Group discussions that focus on sharing personal experiences and emotions
- Collaborative projects that require teamwork and consideration of others’ ideas
- Reflection journals to foster a habit of mindfulness and self-awareness
Research Outcomes on Empathy Development in Schools
Empirical evidence underscores the transformative effect of empathy in education. Studies indicate that students who engage in SEL programs with an emphasis on empathy are more likely to exhibit prosocial behavior, have better academic performance, and navigate social dynamics with greater ease. Truly, by fostering these competencies, we’re not just educating; we’re equipping the next generation with the compass to navigate the world’s complexities with a kind heart and an open mind.
SEL COMPETENCIES
CASEL has identified five interrelated cognitive, affective, and behavioral competencies. The definitions of the five competency clusters for students are:
1. Self-awareness
What Does It Mean to be Authentic? Part of Self-Awareness
Social Emotional Learning (SEL) isn’t just about understanding and managing emotions; it’s about developing the self-awareness that students need to excel both academically and personally. In the bustling environment of a school setting, guiding students towards greater self-awareness can be transformative. This piece shines a light on the pivotal role of SEL in helping students to recognize and refine their own cognitive and emotional processes.
SEL Practices to Advance Student Self-Awareness
Becoming self-aware is a journey, starting with recognizing one’s emotions, thoughts, and values. In schools, SEL can facilitate this through:
- Reflective journaling exercises that encourage introspection
- Regular check-ins where students share their feelings and experiences
- Group discussions that help students articulate their personal growth
- Self-assessment tools that empower students to evaluate their own progress
The Connection Between Self-Awareness and Academic Success
Students who are self-aware are typically better equipped to handle the pressures of academic life. Understanding their own work habits, learning styles, and triggers for stress allows them to navigate challenges more effectively. This clarity can lead to improved focus, better time management, and a more proactive approach to learning. It’s not just about getting better grades – it’s about cultivating a mindset equipped for lifelong learning.
Illustrations of Self-Awareness Journeys in Students
Every student’s journey towards self-awareness is unique. For some, it might be realizing how their background and experiences shape their perspective. Others might discover the root of their anxieties during exams. For example, consider Tara, a ninth-grader who struggled with public speaking. Through SEL activities, she identified her fear as stemming from a desire to be perfect. Recognizing this, she worked through exercises that focused on effort rather than perfection. Gradually, Tara’s confidence grew, and she started participating more in class discussions.
Building self-awareness in the school setting can have far-reaching impacts. As students learn more about themselves, they’re better prepared to tackle life’s challenges and their own educational pathways. With SEL, we’re not just teaching subjects; we’re growing individuals.
2. Self-management
Self-Management (Social Emotional Learning) provides skills associated with self management and how it relates to the teaching principles.
The ability to successfully regulate one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in different situations — effectively managing stress, controlling impulses, and motivating oneself. The ability to set and work toward personal and academic goals.
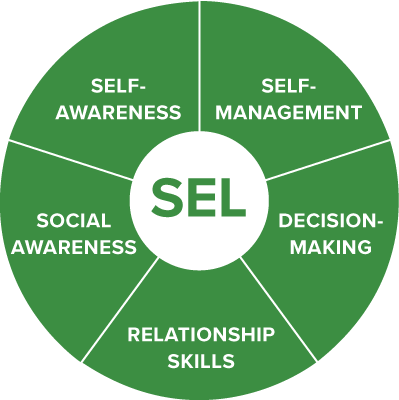
3. Decision-making
DECISION MAKING IN THE CLASSROOM article provides the benefits and importance of decision-making in the classroom. Also the article provides an effective way to teach good decision making.
The ability to make constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions based on ethical standards, safety concerns, and social norms. The realistic evaluation of the consequences of various actions, and a consideration of the well-being of oneself and others.
Social Emotional Learning (SEL) isn’t just about understanding and managing our own emotions; it’s also about forging and maintaining healthy relationships. Relationship skills are a vital component of SEL, empowering students to interact harmoniously with their peers, educators, and the wider community.
Relationship Skills as a Core Element of SEL
Developing relationship skills is essential in the social and educational growth of every student. Through SEL, students learn to communicate effectively, listen actively, cooperate with others, navigate social situations, and resolve conflicts amicably. These skills lay the groundwork for a supportive and inclusive school environment.
Strategies to Improve Peer Relationships and Social Skills
- Encourage team-based activities that require collaboration and communication, helping students practice and refine their interaction capabilities.
- Promote peer mentoring programs where older students support the younger ones, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility.
- Organize social skills workshops to directly teach the nuances of body language, conversation skills, and empathy.
- Implement role-playing exercises to practice real-life social scenarios, aiding students in understanding various perspectives.
Positive Outcomes: Healthier School Relationships through SEL
Integrating relationship-building into the curriculum has clear positive outcomes. Students who master these skills tend to experience fewer conflicts, form deeper connections with their peers, and create a more welcoming school atmosphere. By prioritizing SEL, schools are not just educating students but nurturing well-rounded individuals ready to thrive in all aspects of life.
5. Social awareness
Social Awareness (Social Emotional Learning) provides skills associated with social awareness and why educators should teach social awareness.
The ability to take the perspective of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds and cultures. The ability to understand social and ethical norms for behavior, and to recognize family, school, and community resources and supports.
Unlocking Harmony in the Classroom: SEL-inspired Strategies
Embrace the power of Social Emotional Learning (SEL) and transform your classroom management into an oasis of mutual respect and effective learning. Below, we delve into strategies tailored to nurturing an emotionally healthy educational environment—where students and teachers collaborate with ease and enthusiasm.
Classroom Management through the Lens of SEL
Integrating SEL principles into classroom management isn’t just a concept; it’s a practice that encourages emotional awareness and responsible decision-making. By emphasizing empathy, we create a classroom culture where every student feels valued and understood, paving the way for smoother daily interactions and fewer behavioral disruptions.
Techniques for Creating an Emotionally Healthy Classroom
- Establish Clear Expectations: Begin by setting clear, attainable goals for both behavior and academic achievement, ensuring every student knows what’s expected of them.
- Model Emotional Intelligence: As a teacher, lead by example. Showcase active listening, patience, and empathy to inspire your students to do the same.
- Encourage Reflection: Reserve time for students to reflect on their emotions and actions, helping them to develop self-regulation skills.
- Create Inclusive Activities: Design cooperative projects that require team effort and respect for diverse opinions—key skills in SEL.
Check out the following posts related to Social Emotional Learning:
Effective SEL Teaching Practices You Need to know In the Classrooms
What You need to Know SEL Lesson Planning
SEL as Empowerment

Teachers are responsible for instructing students on the process of making informed decisions on the various choices and problems they encounter. A student with exceptional subject matter expertise, but deficient social or problem-solving abilities, is susceptible to manipulation. Likewise, students who can anticipate the outcomes of their activities may be more adept at making sound judgments.
Social and emotional learning encompasses more than just preventing students from getting into trouble. It involves cultivating life skills that can be used in various contexts, according to authors Douglass Fisher, Nancy Frey, and Dominique Smith of the book All Learning Is Social and Emotional Learning.
Fisher, Frey, and Smith hope students will learn how to identify problems, analyze problems, and solve problems. To do so, they need to confront a wide range of challenges that are academic, social, and emotional—and their teachers need to equip them with the right tools to engage in these processes. Authors intent is to provide teachers with a toolbox of strategies that will help transform students into empowered, all-purpose problem solvers.
Fisher, Frey, and Smith strongly emphasize that classroom teachers play a vital role in the integration of social and emotional learning (SEL), and that their purposeful actions to cultivate students’ social and emotional abilities are of utmost importance. Partly, because teachers are already involved in this form of education with pupils through an implicit curriculum. However, authors also express this sentiment due to the number of pupils who require these talents to achieve success.
SEL and Equity
It is crucial to emphasize that social and emotional learning encompasses far more than simply cultivating children who exhibit kindness, cooperation in the classroom, and active participation in civic matters. Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) is also a matter of fairness and equality.
Fisher, Frey, and Smith strongly believe that students’ behavior is due to poverty, neglect, and abuse, which all influence a child’s ability to learn. However, we must not allow our inability to eliminate these circumstances to serve as a justification for taking no action whatsoever. We can recognize the existence of these circumstances and make deliberate efforts to mitigate their effects.
Integrated SEL
Authors organized “big ideas” contained under the umbrella of SEL into five broad categories:

Identity and Agency:
Children’s and adolescents’ sense of identity is shaped by a myriad of factors, including experiences inside and outside school. Their identity materially governs their agency, which is their belief in their ability to influence the world around them.
Blog Post: Identity and Agency Important Foundation of a Human Being
Emotional Regulation:
We often hear about the importance of mindfulness in our personal lives, but how often do we consider its powerful role within educational settings? By incorporating mindfulness into the school curriculum, educators open up a new dimension of Social Emotional Learning (SEL) that can significantly benefit students and teachers alike.
Benefits of Mindfulness Practices in Schools
Mindfulness practices are not just a trend; they are evidence-based techniques that have been shown to offer myriad benefits in educational environments. From reducing stress and anxiety to enhancing attention spans, mindfulness is making a noticeable difference in classrooms around the globe.
- Decreased stress and anxiety levels
- Improved concentration and attention
- Better emotional regulation among students
- Enhanced conflict resolution abilities
- Strengthened resilience and coping skills
How Mindfulness Supports Emotional Regulation and Focus
At its core, mindfulness teaches students to be present and aware of their emotions and thoughts. By encouraging children to focus on the moment and accepting feelings without judgment, mindfulness equips them with the tools necessary for effective emotional regulation. This is essential for creating a learning environment that fosters calm, focused, and engaged students.
Integrating Mindfulness into the School Curriculum
So, how can schools practically bring mindfulness into the classroom? It’s simpler than you may think, and it doesn’t require a complete overhaul of existing lesson plans. Here are a couple of ways to get started:
- Daily Mindfulness Moments: Start or finish each day with a short mindfulness exercise, such as deep breathing or a guided visualization.
- Mindful Movement: Incorporate gentle yoga or stretching sessions that prompt students to pay attention to their movements and the sensations in their bodies.
- Reflection Time: Allow time for students to reflect on their thoughts and feelings, which can be facilitated through journaling or open discussions.
Integrating mindfulness into education doesn’t just create a more conducive learning environment; it helps build a foundation for a more emotionally intelligent and attentive future generation.
Cognitive Regulation:
Learning isn’t passive. Acquiring knowledge and skills requires students to engage in certain habits and dispositions.
Social Skills:
Quality relationships are the basis for effective interactions inside and outside school, because they allow productive and positive collaboration. Students need to be equipped with tools to foster, maintain, and repair relationships, and this requires substantial adult guidance.
Public Spirit
This final aspect of our integrated SEL model is the basis for a democratic way of life, and essential to creating and sustaining a social structure in which people are valued and treated fairly. We see public spirit evidenced in the ways that people contribute to and steward their communities.
Keep Learning
How to Embed SEL Into Your Instruction
Final Thoughts: The Long-Term Value of SEL
It’s essential to take a moment and reflect on the profound and enduring impact that SEL can have on both students and the wider education system. SEL isn’t just a temporary fix; it’s a transformative process that invests in the future of every child.
Imagine a classroom where empathy and cooperation are as commonplace as textbooks and pencils. Picture a school where conflicts are resolved with understanding and respect. This is the power of SEL—creating an environment where learning thrives alongside emotional and social growth.
- With SEL, students gain an emotional toolkit that helps them navigate challenges both in and out of the classroom.
- Educators become equipped to foster a learning atmosphere that’s not just academically encouraging but also emotionally supportive.
- Schools transform into inclusive communities where every student feels valued and understood.
Social Emotional Learning is about shaping a healthier, more compassionate generation with the skills to create a positive ripple effect in our society. Every lesson in empathy, every exercise in self-awareness, every strategy in relationship-building, are threads weaving a stronger social fabric for years to come.
My hope is that schools are committed to this vision, not just as a goal, but as a journey we are proud to embark on with educators, students, and parents alike. Our dedication to Social Emotional Learning stems from the belief that these are not just life skills—they are the foundation of a more empathetic, understanding, and emotionally intelligent world.